India stands at a critical inflection point. As the nation targets becoming a $5 trillion economy by 2025, industrial engineering must evolve from traditional manufacturing practices to integrate smart automation in industrial engineering with sustainable infrastructure. This transformation isn’t just optional it’s essential for global competitiveness and meeting environmental commitments.
The challenge is clear: how can India’s industrial sector simultaneously increase productivity, reduce costs, and minimize environmental impact? The answer lies in integrating cutting-edge automation technologies with sustainable practices that align with India’s climate goals and the evolving demands of global supply chains.
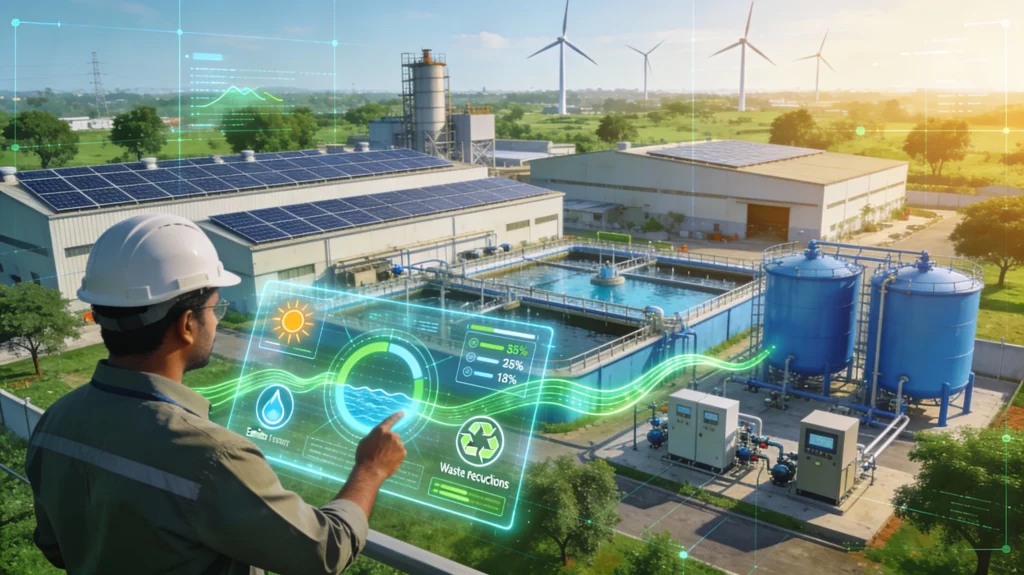
The Current State of Indian Industrial Engineering
India’s industrial engineering sector employs over 12 million people and contributes significantly to GDP. However, many Indian manufacturers still rely on legacy systems that lack efficiency, scalability, and sustainability measures. According to recent industry reports, 60% of Indian manufacturing facilities operate below international efficiency benchmarks.
The gap stems from several factors: limited adoption of IoT in industrial engineering, insufficient investment in digital infrastructure, and the high initial costs of technology implementation. Yet 2025 marks a turning point as government initiatives, competitive pressures, and technological affordability converge to make transformation achievable.
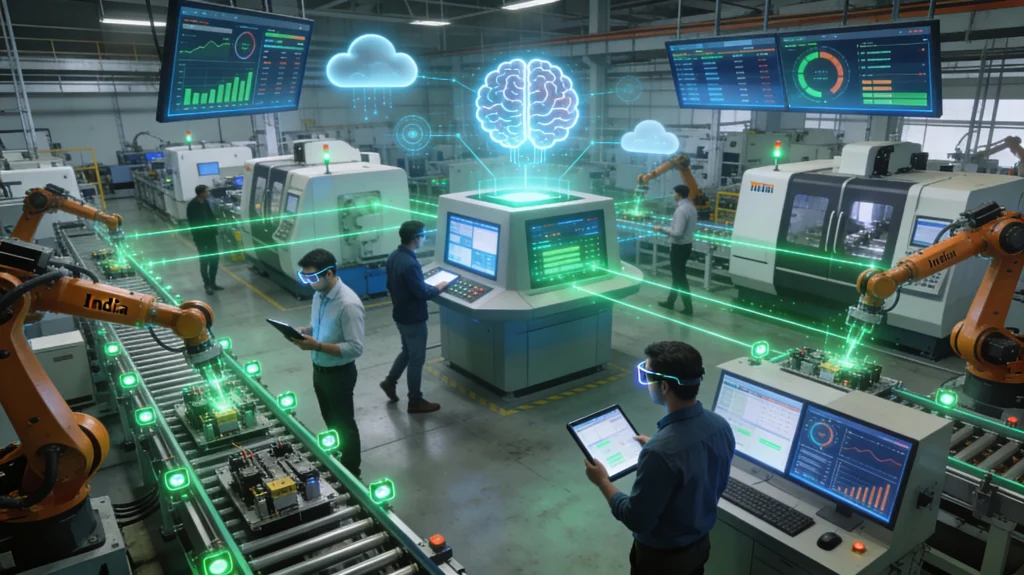
Smart Automation: The Core Transformation
Smart automation in industrial engineering represents the convergence of IoT, artificial intelligence, and traditional manufacturing expertise. Unlike simple automation of the past, smart systems learn, adapt, and optimize operations in real-time.
- Real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance: Sensors track equipment health and predict failures before they occur, reducing downtime by 30-40%
- Autonomous decision-making: AI algorithms optimize production parameters without human intervention
- Supply chain visibility: Connected systems provide end-to-end visibility from raw materials to finished products
- Quality assurance through data analytics: Continuous monitoring ensures consistent output quality
- Remote operations: Engineers can manage facilities across geographic locations
Manufacturing companies implementing industrial automation solutions report productivity gains of 20-35%, reduced operational costs by 15-25%, and improved worker safety through hazard reduction. This translates to millions in annual savings for mid-sized manufacturing facilities.
Sustainable Infrastructure: Beyond Compliance
Sustainability in industrial engineering isn’t merely environmental responsibility—it’s increasingly a business imperative. Global supply chains now demand sustainable practices, and India’s government has set aggressive targets including achieving net-zero emissions by 2070.
1. Energy Efficiency Through Renewable Integration
Integration of renewable energy integration in manufacturing addresses both cost and environmental concerns. Solar panels on factory rooftops, combined with smart grid technology, enable industries to reduce electricity costs by 30-40% while decreasing carbon footprints. The combination of solar systems with intelligent load management creates resilient, self-sufficient industrial facilities that operate efficiently regardless of grid conditions.
2. Water Conservation and Wastewater Management
Industrial facilities consume enormous quantities of water. Modern water treatment automation for STP/ETP/WWTP can reduce water consumption by 50% while ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. These systems use PLC-based controls and real-time monitoring to optimize chemical dosing and filtration, ensuring both efficiency and quality.
3. Waste Reduction and Circular Economy Practices
Smart manufacturing minimizes waste through precision control, material tracking, and recycling optimization. Advanced analytics identify inefficiencies in material usage and enable circular economy practices where waste from one process becomes input for another, creating zero-waste manufacturing ecosystems.

India’s Industrial Engineering Opportunity in 2025
India has distinct advantages in this transition:
Demographic dividend: A young, tech-savvy workforce ready to embrace new technologies and methodologies—India’s average engineer age is 32, ensuring rapid adoption of Industry 4.0 concepts.
Cost advantages: Compared to developed nations, Indian industrial automation solutions are 40-50% cheaper to implement, making it an attractive hub for global manufacturers seeking cost-effective yet high-quality solutions.
Government support: The Indian Industrial sector receives incentives through PLI schemes, Infrastructure Development Fund, and R&D tax credits encouraging technology adoption and innovation.
Entrepreneurial ecosystem: A thriving startup scene creates innovative automation solutions tailored to Indian manufacturing needs, from SME-friendly platforms to enterprise-scale systems.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
Skill gaps: India needs certified professionals trained in Industry 4.0 technologies. Investing in workforce development through partnerships with educational institutions is critical for scaling adoption.
Capital requirements: While technology costs are declining, upfront investments remain substantial. Creative financing through government schemes and vendor partnerships can bridge this gap effectively.
Legacy system integration: Retrofitting old equipment with smart systems requires careful planning, but hybrid solutions make this achievable without complete facility shutdown.
Cybersecurity: Connected systems create vulnerabilities requiring attention. Robust cybersecurity protocols, regular security audits, and industry-standard encryption are essential safeguards.
The Path Forward
India’s industrial engineering sector at the inflection of 2025 faces a clear choice: embrace transformation or risk obsolescence in an increasingly competitive global marketplace. The future belongs to manufacturers who can simultaneously optimize for cost, quality, sustainability, and flexibility—and this is precisely what smart automation + sustainable infrastructure delivers.
The integration of advanced automation technologies with environmental responsibility isn’t a distant future vision. It’s happening now, and organizations that move decisively in 2025 will capture disproportionate competitive advantage as the decade progresses.
5 FAQs
Q1: What’s the average ROI for implementing smart automation?
Most industrial facilities see 200-300% ROI within 3-5 years through productivity gains, reduced maintenance costs, and energy savings.
Q2: Is smart automation suitable for small and medium enterprises (SMEs)?
Yes. Modular industrial automation solutions and cloud-based monitoring make smart automation accessible to SMEs with lower capital requirements and faster implementation.
Q3: How long does industrial automation implementation take?
6-18 months depending on facility complexity, ranging from assessment to full operational deployment and optimization of all systems.
Q4: What workforce skills are needed for smart automation?
Combination of mechanical engineering, electrical expertise, IoT programming, data analytics, and cybersecurity knowledge tailored to manufacturing contexts.
Q5: How does renewable energy integration improve manufacturing efficiency?
Renewable energy integration reduces operational costs by 30-40%, improves sustainability metrics, and enables energy-independent manufacturing through smart load management and battery storage.






