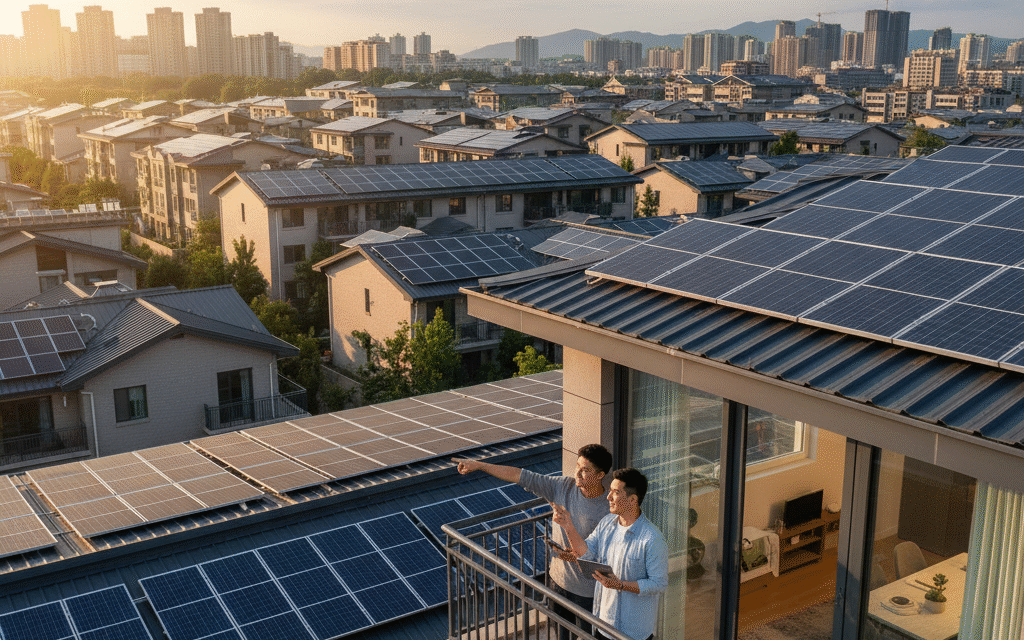
China’s rooftop solar revolution is transforming rural and urban landscapes alike, offering valuable insights for residential solar adoption globally. From innovative financing models to cutting-edge safety technology, Chinese innovations are creating a blueprint for sustainable energy access that homeowners everywhere can learn from.
The Numbers Tell the Story
China installed a record-breaking 36 GW of rooftop solar in Q1 2025 alone, marking the largest quarterly capacity addition for distributed PV in the country’s history. This surge was driven by new National Energy Administration guidelines that encourage self-consumption to reduce grid congestion and support China’s dual carbon targets.
The scale of opportunity is staggering. China’s rural areas possess 27.3 billion square meters of rooftop space, with potential for nearly 2 billion kW of installed capacity and annual electricity generation exceeding 2.5 trillion kWh. This represents nearly one-third of China’s total national electricity consumption.
Revolutionary Financing Models Transform Access
The Rooftop Leasing Advantage
Over 80% of China’s residential solar market operates under a rooftop leasing model, particularly prevalent in rural areas. Homeowners contribute unused roof space and earn reliable rental income while developers handle installation, maintenance, and grid integration costs.
This model offers several key advantages:
- Zero upfront costs for homeowners
- Guaranteed annual income of 3,000-3,500 yuan ($430-500) per household
- Professional maintenance and insurance coverage
- Village-level aggregation that reduces soft costs through economies of scale
Community Solar Bonds and Group Purchasing

Chinese developers are pioneering community solar financing through group purchasing programs that reduce individual costs by 22%. Village-wide installations in areas like Xuzhou’s Shuangjing Village generate over 6.4 million yuan in lifetime revenue while cutting construction and maintenance expenses significantly.
Smart Inverter Technology Sets New Safety Standards

AFCI Technology Prevents Fire Hazards
Chinese manufacturers like Solis, Huawei, and Sungrow are leading the world in Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter (AFCI) technology that can prevent up to 99% of power station fire risks. These smart inverters detect and shut off dangerous electrical arcs within 0.5-1.5 seconds, far exceeding international safety requirements.
Key AFCI innovations include:
- AI-powered arc detection using deep learning algorithms
- Support for DC currents up to 60A with cable loops extending 650 meters
- Real-time monitoring through IoT-enabled microinverter networks
- Component-level fault location for precise troubleshooting
Microgrids Enable Energy Independence
Beijing suburban areas and industrial parks are implementing solar microgrids that combine rooftop PV with energy storage systems. These self-sufficient networks can:
- Generate 7 million kWh annually for entire industrial complexes
- Replace 2,800 metric tons of coal consumption per year
- Cut carbon emissions by 7,500 tons annually
- Reduce energy costs by over 20% for participating businesses
Government Support Accelerates Adoption

The Whole County PV Programme
China’s Whole County PV Programme targets installation on:
- 50% of government buildings
- 40% of public buildings (schools, hospitals)
- 30% of commercial spaces
- 20% of rural households
This coordinated approach has registered 676 counties from 31 provinces, benefiting 140 million people and adding 87.4 GW of distributed capacity in 2022 alone.
Poverty Alleviation Through Solar
The Solar Energy for Poverty Alleviation Programme (SEPAP) provided solar installations to 4.18 million impoverished households, exceeding its original 10 GW target by installing 26 GW of capacity. Poor families receive 100% subsidies with zero or low-cost financing options.
Environmental and Economic Impact

Carbon Reduction at Scale

China’s distributed solar boom is contributing to a 1.6% drop in CO2 emissions in 2025, with wind and solar generating 26% of the country’s electricity by April 2025 – the highest monthly share ever recorded.
Rural Economic Transformation

Lessons for Global Implementation
Economies of Scale Matter
The Chinese model demonstrates that single-supplier county-wide tenders can dramatically reduce soft costs compared to individual installations. This approach addresses one of the biggest barriers to residential solar adoption worldwide.
Technology Integration is Key
Combining solar PV with smart home automation, heat pumps, and energy storage creates comprehensive energy solutions. Chinese homes are increasingly using solar-driven IoT systems for real-time optimization and peak-shaving.
Community-Centric Approach Works
Village-level aggregation and community solar models ensure that even households without suitable roofs or financial resources can benefit from clean energy access. This inclusive approach maximizes social and environmental impact.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How much can homeowners earn from rooftop leasing in China?
A: Under China’s rooftop leasing model, homeowners typically earn 3,000-3,500 yuan ($430-500) annually from leasing their roof space, with developers handling all costs and maintenance.
Q2: What makes Chinese smart inverters safer than traditional models?
A: Chinese AFCI-enabled inverters use AI-powered arc detection to identify and shut off dangerous electrical faults within 0.5-1.5 seconds, preventing up to 99% of fire risks in solar installations.
Q3: How does the village-level aggregation model work?
A: Entire villages coordinate solar installations through single-supplier tenders, reducing costs by 22% through economies of scale while enabling grid integration solutions that individual homes couldn’t achieve.
Q4: What is China’s target for rural rooftop solar coverage?
A: China’s Whole County PV Programme aims to install solar on 20% of rural households, alongside higher percentages for commercial and government buildings, benefiting 140 million people across 676 counties.
Q5: How do Chinese solar microgrids achieve energy independence?
A: Solar microgrids combine rooftop PV with energy storage systems to create self-sufficient networks that can operate independently or sync with the main grid, providing flexible, stable, and environmentally friendly power.
Q6: What financing options are available for rural Chinese households?
A: Rural households can choose between rooftop leasing (80% of market) with zero upfront costs, or self-financing models offering higher returns (13-15% ROI) but requiring ownership of equipment and maintenance responsibilities.
Q7: How does China’s solar program support poverty alleviation?
A: The Solar Energy for Poverty Alleviation Programme provided 100% subsidies and zero-cost financing to 4.18 million impoverished households, installing 26 GW of capacity and generating reliable income streams.
Q8: What role do community solar bonds play in financing?
A: Community solar bonds and group purchasing programs enable villages to collectively invest in solar projects, reducing individual costs while creating shared ownership models that benefit entire communities.






